4 Different Types of Car Headlights (With Pictures)
Photo: housegrail.com
Since the days of horse-drawn carriages and only mounted oil lamps for night travel, car headlights have evolved into a highly sophisticated technology. Our ancestors did not have to worry about modern problems like traffic or high speeds, and headlights have moved on with the times.
Driving at night has become safe and easy with the advent of powerful and directed headlights. Getting from A to B in the dark is now both easier and safer than ever. But there are a few different types of headlights to consider before purchasing.
We detail the four most common types and see which option shines the brightest, both for your safety and for your pocket.
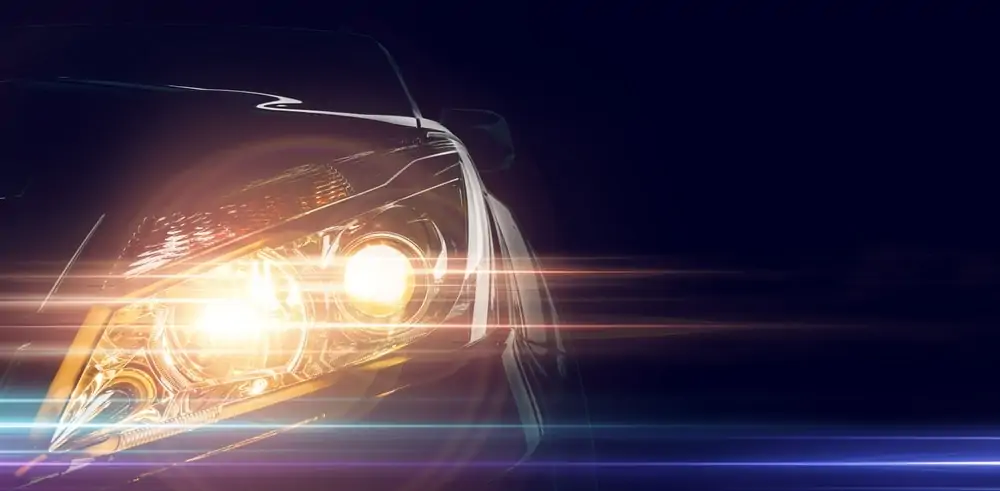

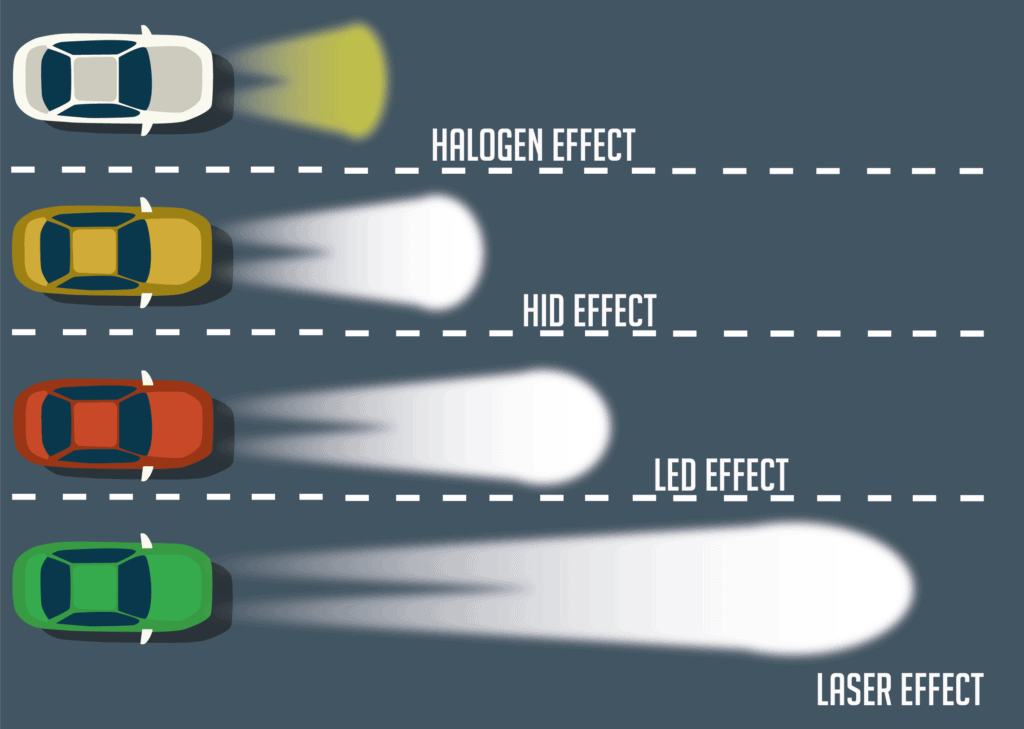
Halogen Car Headlights
1. Halogen Car Headlights
Halogens are the most common types of headlights on cars. But their popularity and usage have started to dim. They can be seen as the old and weathered grandfather of headlights, being slowly outperformed and replaced by youthful new inventions.
They use different gases and a tungsten filament housed in a heatproof glass casing. The filament is heated via an electrical current, which is what produces light. Halogens come in two different classifications: standard and projector. A standard headlight uses forward-facing bulbs enclosed in a reflective casing, beaming the light outward and forward. A projector light uses a rear-facing bulb onto a reflective casing, for a more directed and focused beam output.
Halogens are cheap and widely available, making them easy to replace. However, they are fairly inefficient and dim when compared to the newer types of lights available. Because they heat up so much, much of their potential energy is wasted, making them inefficient, especially when compared to energy-saving LEDs.
They are also fairly sensitive, and even the smallest contact with your hands will dramatically decrease their heat distribution and thus, lower their efficiency and lifespan.

HID Car Headlights
2. HID Car Headlightsl
High Energy Discharge(HID) headlights, also known as Xenon headlights, are being adopted by a high proportion of car manufacturers, outshining the competition. This is mainly because they are roughly two to three times brighter than the aging halogen lamps and last a good deal longer.
HIDs are somewhat similar to halogens in that they also use gases — Xenon gas, in this case — and a tungsten filament to cause illumination. However, with HIDs, there is no heating involved. It is the usage of Xenon gas alone that causes the light.
Not only does Xenon sound futuristic, but it also makes your headlights beam a distinctly blue-tinged beam. Their brighter lumen rating makes them a safer option, illuminating far more of the road at night than halogens or LEDs. However, this intense brightness can also be a drawback. Oncoming drivers often complain of being blinded by them.
A drawback of HIDs is their high cost. This is mostly due to the rare metals and gases used in their production. They can also take a few minutes longer than halogens to reach full brightness, but once they do, they use significantly less energy to stay running.
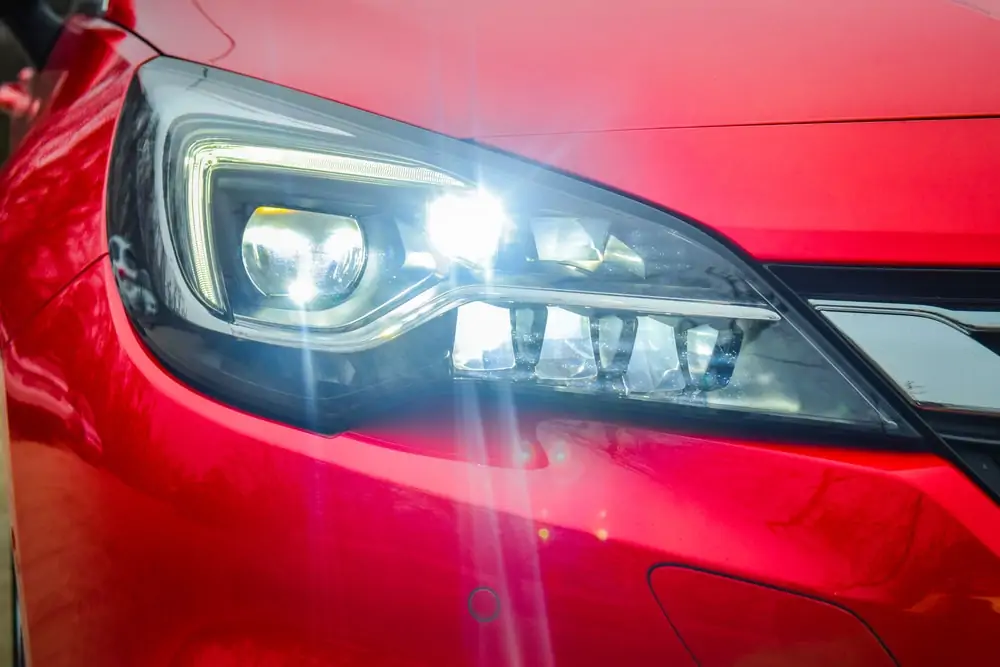

LED Car Headlights
3. LED Car Headlights
LEDs, or Light Emitting Diodes, are the new kids on the block of illumination, their biggest drawcard being efficiency. LEDs use significantly less power than both halogens and HIDs. They also have an incredibly long lifespan, ones that could theoretically outlast the vehicle they are installed in. Because they are so small, they can be arranged in virtually any shape, making them infinity customizable. This has resulted in many unique headlamp designs in the last decade.
LED lights are commonly used on tail lights due to their small size and customization capabilities. LEDs do produce a significant amount of heat when running. This requires an extra heat control system at the bottom of each light, which accounts for their expense and low market use.
Being so new to the market, they are quite expensive. The lack of demand has resulted in little construction innovation and driven up the cost due to the need for handmade components. But this is swiftly changing, and LEDs are well on the way to becoming the standard headlights in the motor industry.
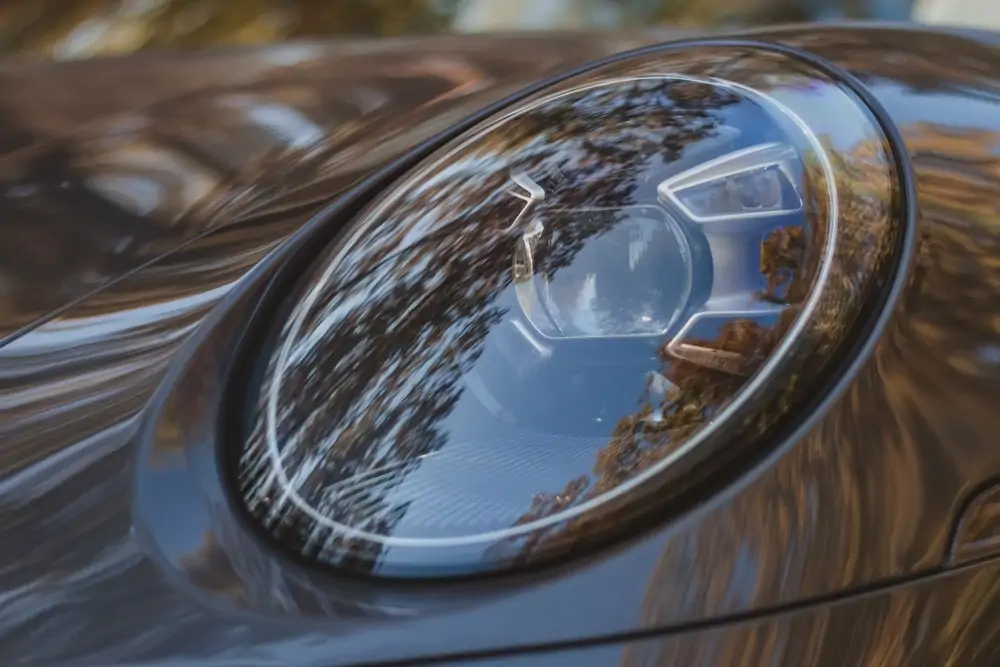

Laser Car Headlights
4. Laser Car Headlights
Laser lights are a brand-new technology, with only a small number of (very expensive) vehicles boasting their use.
The light being emitted from the headlamp does not come directly from the laser. The laser is used in place of electricity in order to excite a gas that then produces the light, similar to HIDs. Laser headlights are the future of headlamp technology. Their small size allows them to be used in infinite shapes and even reduce the physical size of the front headlamp to space-age compactness.
However, they are far more expensive than any other lamp listed here and are only available on very high-end vehicles. They also use more power, though with new technology, this could be drastically reduced in the future.
4 Types of Car Headlights
In Summary
Laser lights are still a few years away from being wildly available and affordable. LEDs, on the other hand, are moving up through the car world and becoming a popular and efficient option. Their use is likely to become standard practice in the near future due to their adaptability and energy-saving draw.
HIDs and Halogen lights are still quite common and are cheap, functional options for the average motorist. They provide the essence of what every driver needs in the dark: light. This makes them an obvious choice until cost can catch up to technology, and we can all have lasers beaming out of the front of our vehicles.







